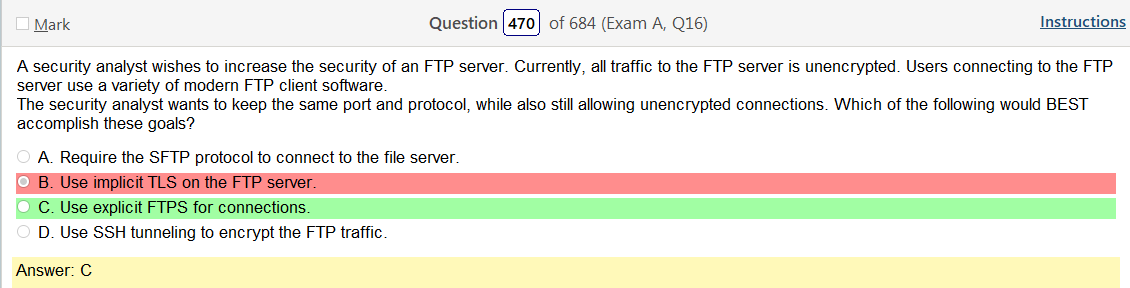
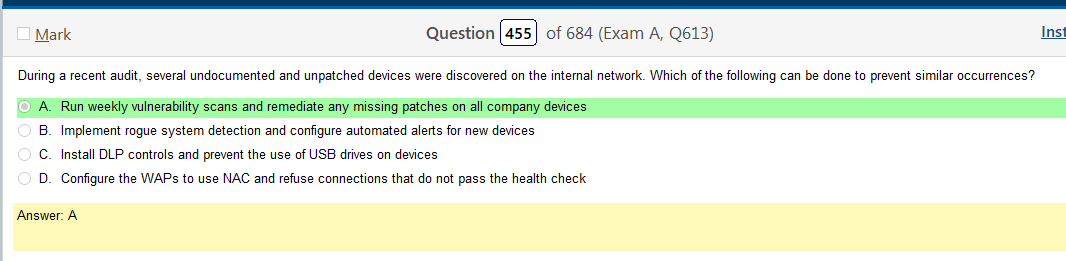
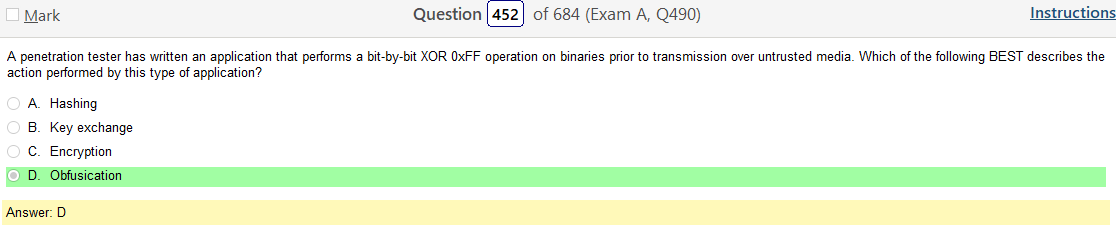
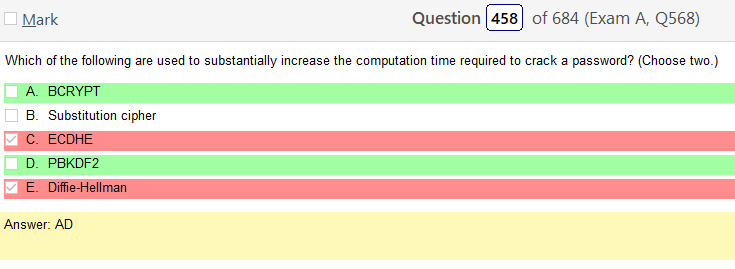
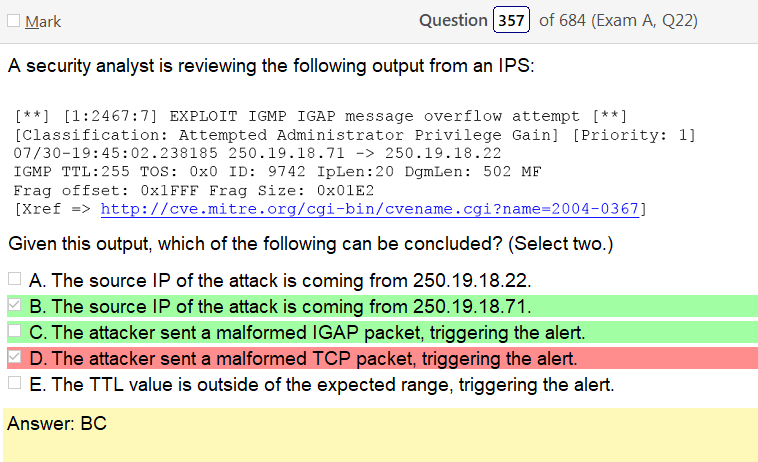
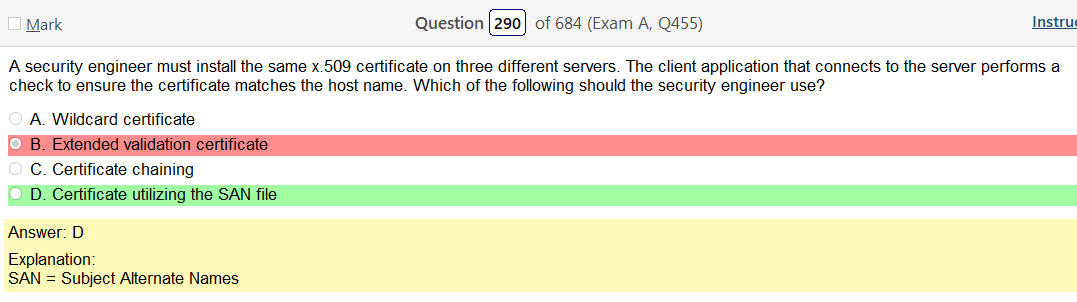
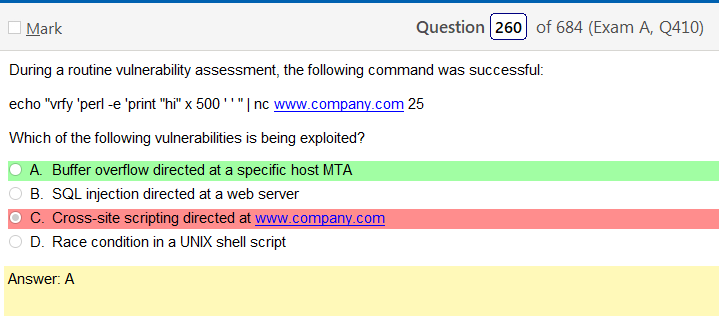
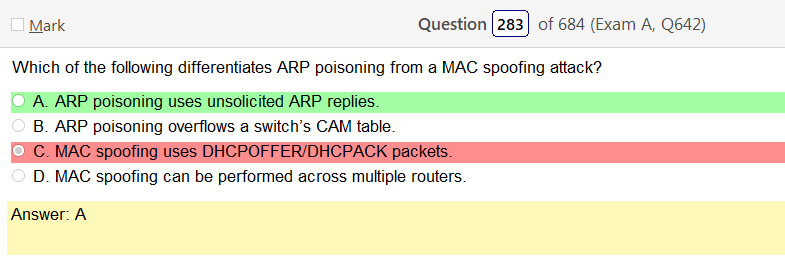
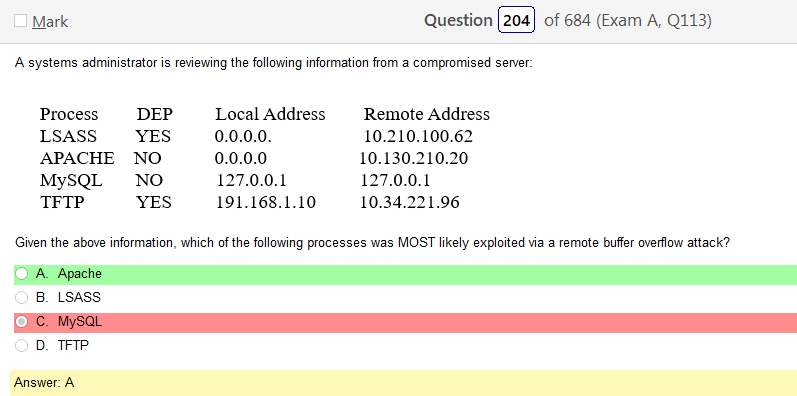
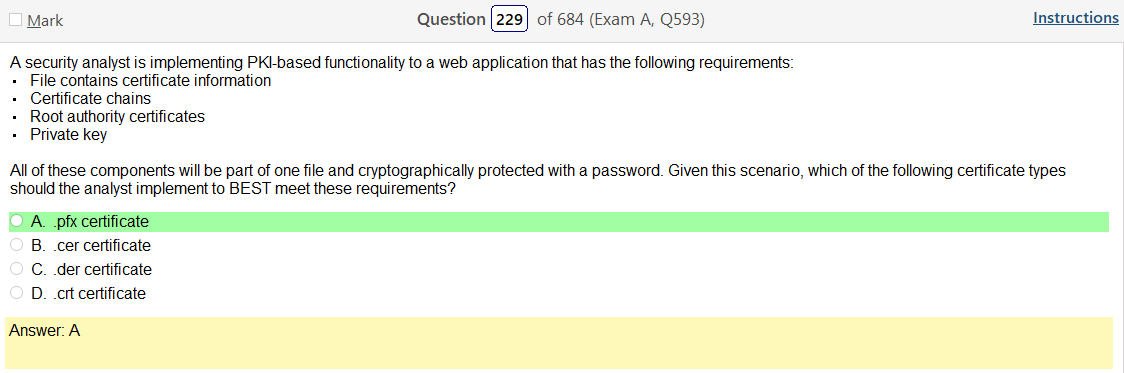
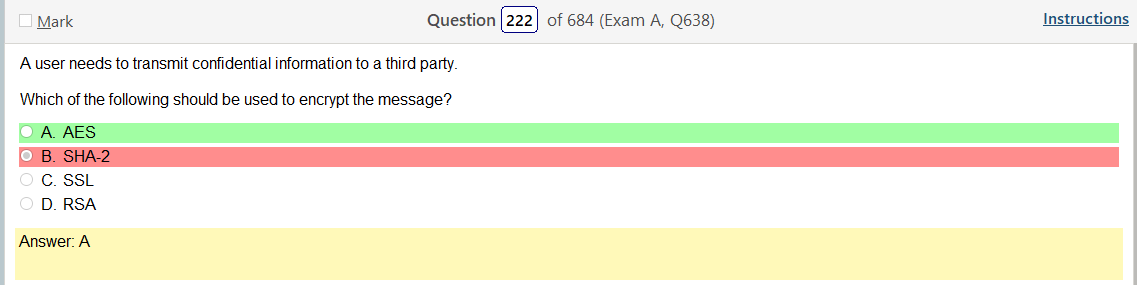
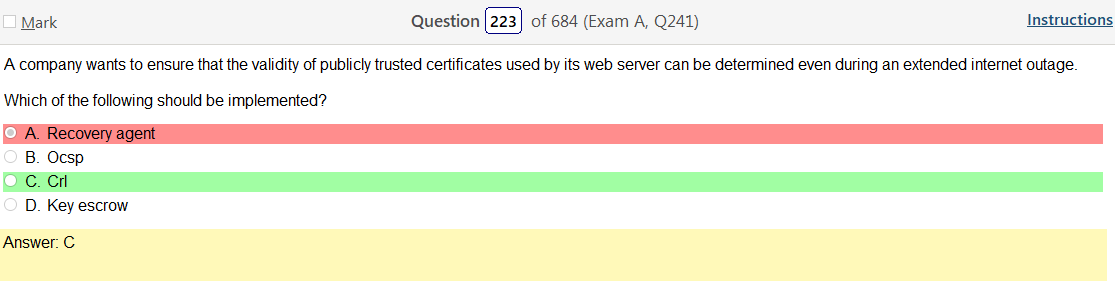
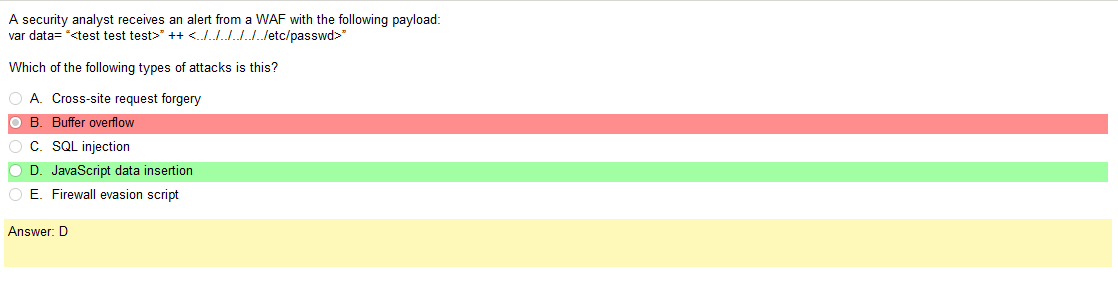
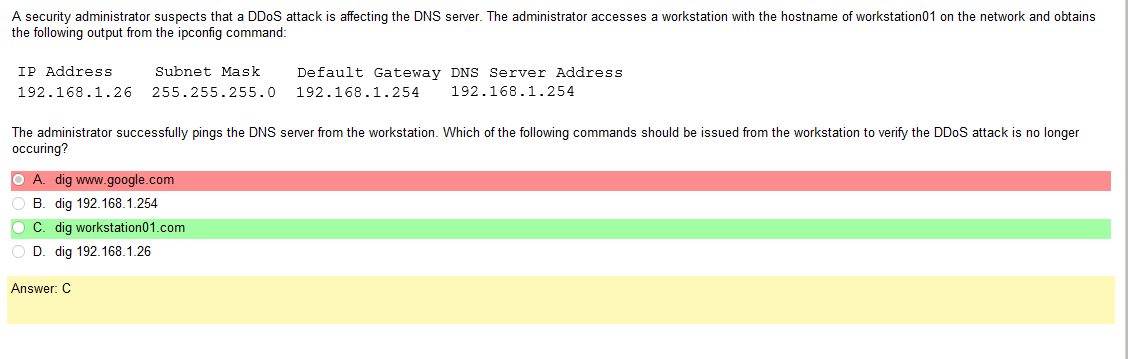
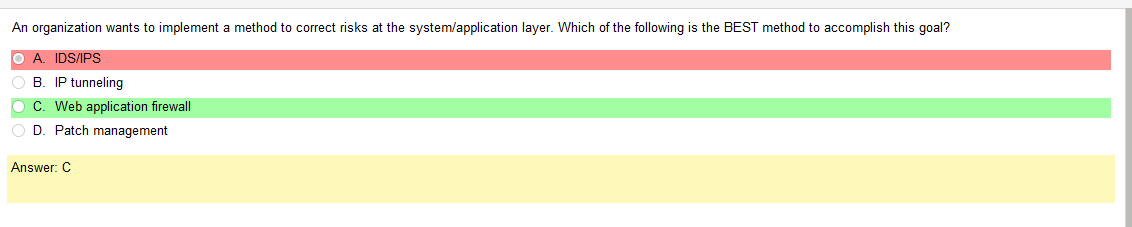
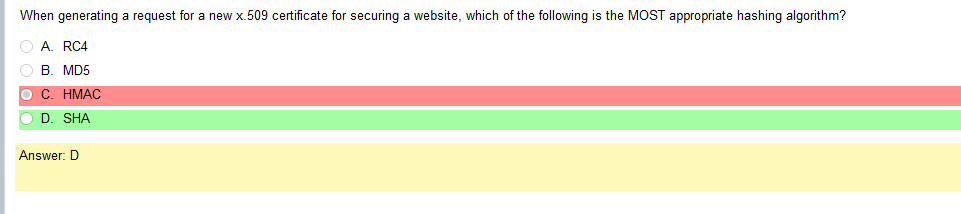
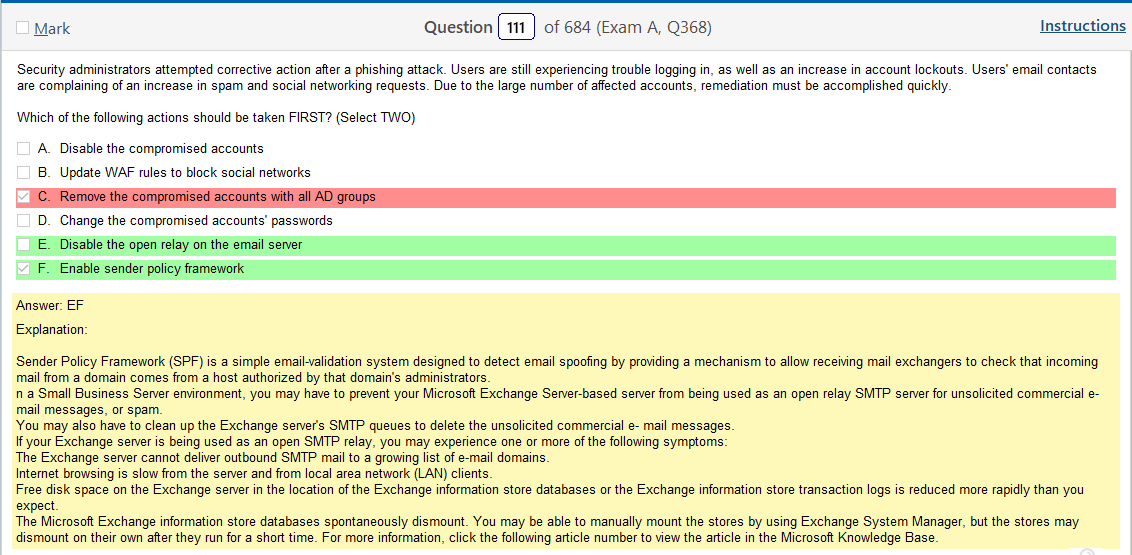
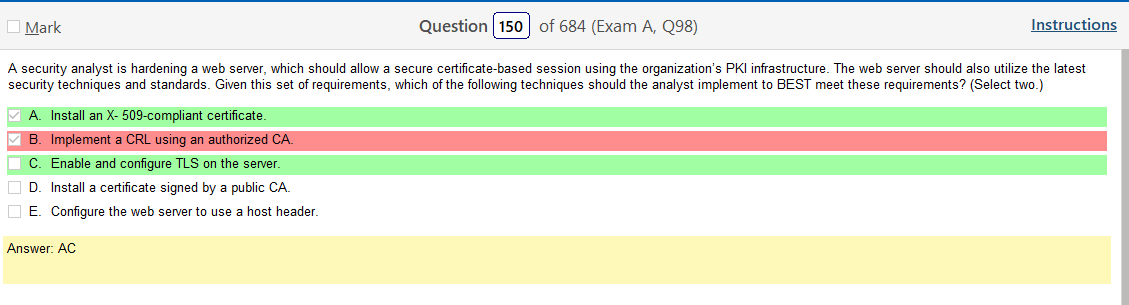
Alright, another day, another day of learning. Exciting times.

Again, I fail to know enough about these technologies to provide an educated opinion.
- Open ID Connect – OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an authentication layer on top of OAuth 2.0, an authorization framework.[1] The standard is controlled by the OpenID Foundation.
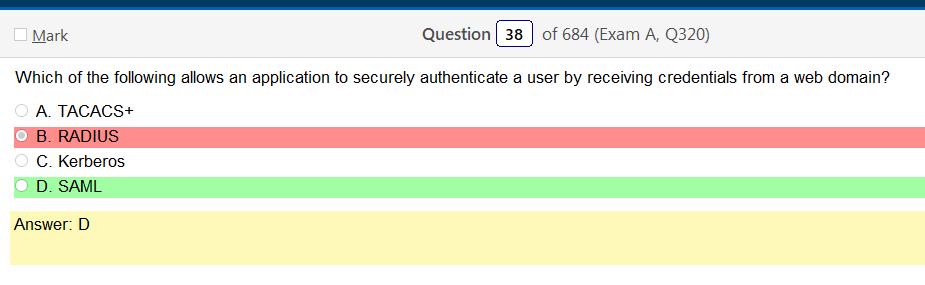
- SAML – The single most important use case that SAML addresses is web-browser single sign-on (SSO). Single sign-on is relatively easy to accomplish within a security domain (using cookies, for example) but extending SSO across security domains is more difficult and resulted in the proliferation of non-interoperable proprietary technologies. The SAML Web Browser SSO profile was specified and standardized to promote interoperability.[2] (For comparison, the more recent OpenID Connect protocol[3] is an alternative approach to web browser SSO.)
- XACML – “eXtensible Access Control Markup Language”. The standard defines a declarative fine-grained, attribute-based access control policy language,[2] an architecture, and a processing model describing how to evaluate access requests according to the rules defined in policies.
- LDAP – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP /’?ldæp/) is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network.[1] Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network
- OAuth 2.0 – OAuth provides to clients a “secure delegated access” to server resources on behalf of a resource owner. It specifies a process for resource owners to authorize third-party access to their server resources without sharing their credentials. Designed specifically to work with Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), OAuth essentially allows access tokens to be issued to third-party clients by an authorization server, with the approval of the resource owner. The third party then uses the access token to access the protected resources hosted by the resource server.[3]
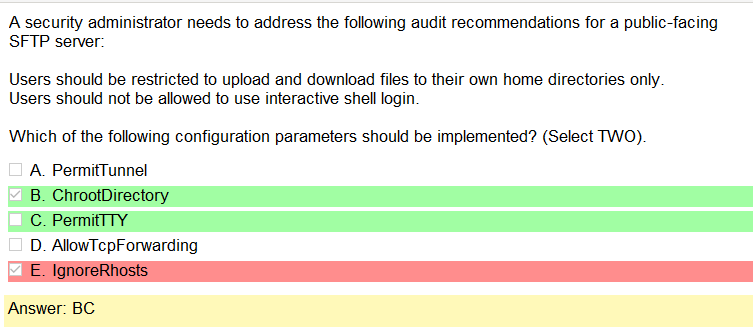
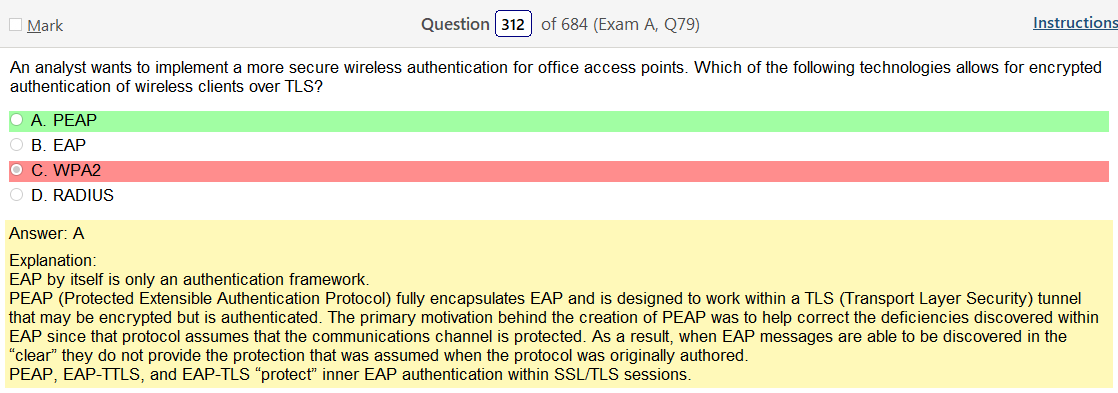
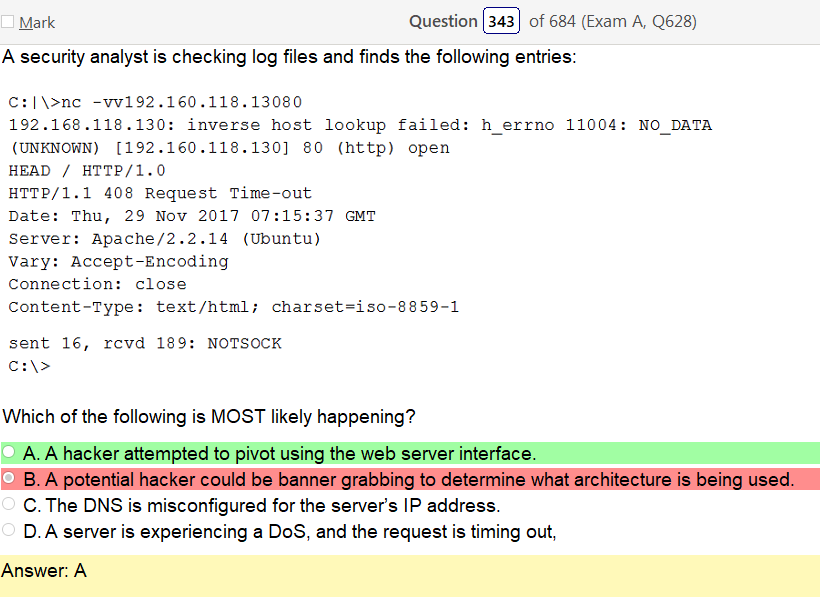
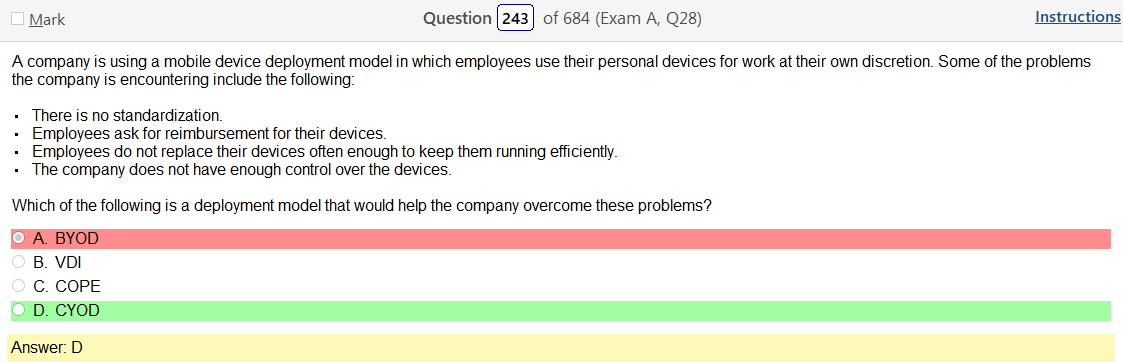
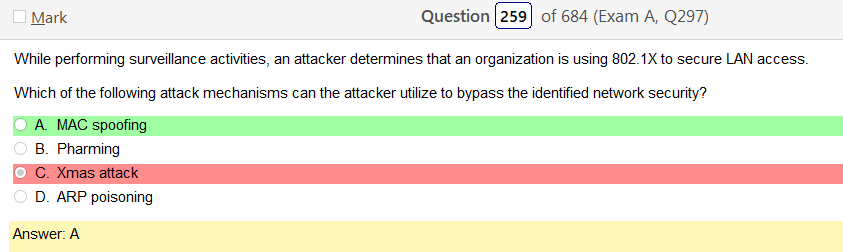
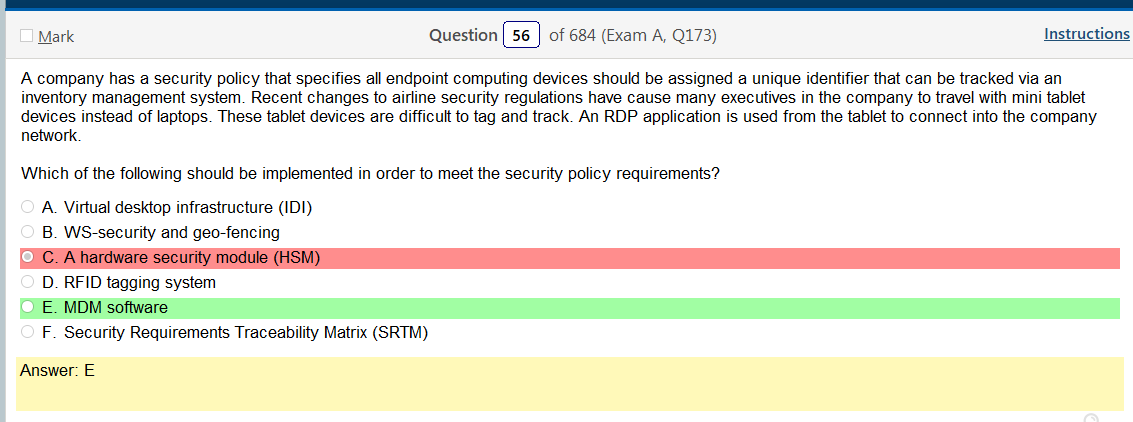
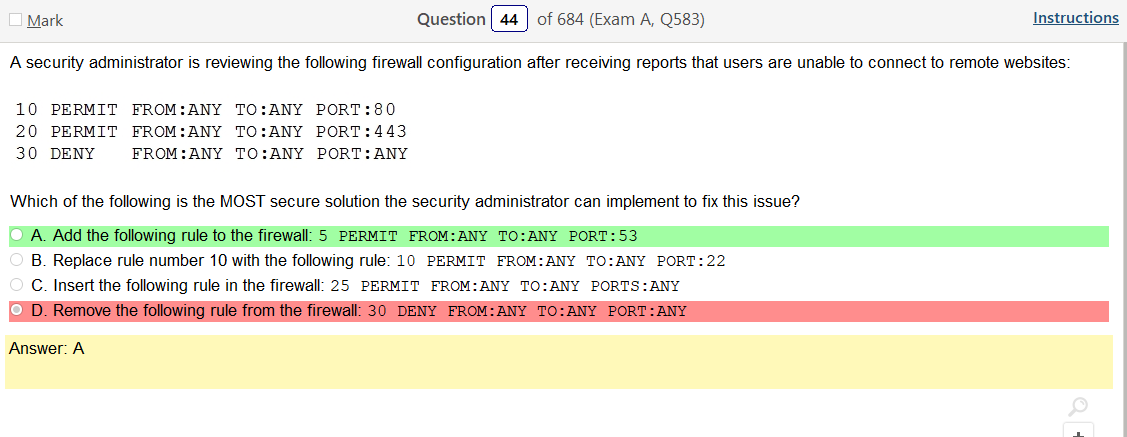
So based on the answer Open ID Connect seems really obvious on account of the naming conventions. However normally with an authentication provider there is more detail as to how the process actually works and if the passwords are hashed. So on and so forth. Now, in regards to detail I’m finding my self wanting more. Now looking at SAML its saying that OpenID Connect is basically the same thing. Moving on to XACML, this is a big one. Its not SSO related but has a ton of information and complicated diagrams on how auth requests are processed but nothing about appropriate hashing or encryption. It’s almost like they are going into NAC type of strings. To be honest this is not very helpful other than knowing its not SSO focused and uses some sort of policies that seem overlapping. LDAP, here is says we can use TLS for cert based auth or kerberos. I’m starting to get a grasp on this. It’s honestly so much more fun to actually learn material rather than simply rush through it. Oauth is really straight forward. Inter platform SSO provider.
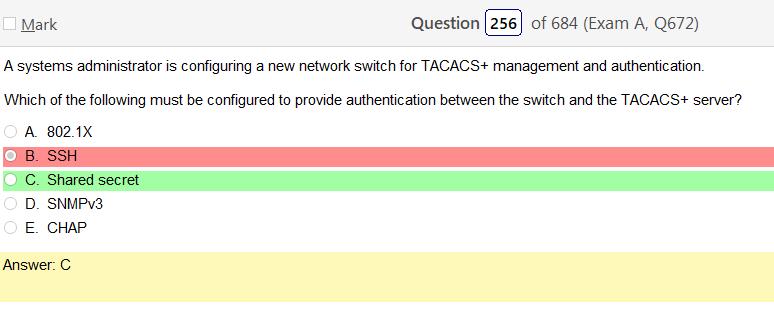
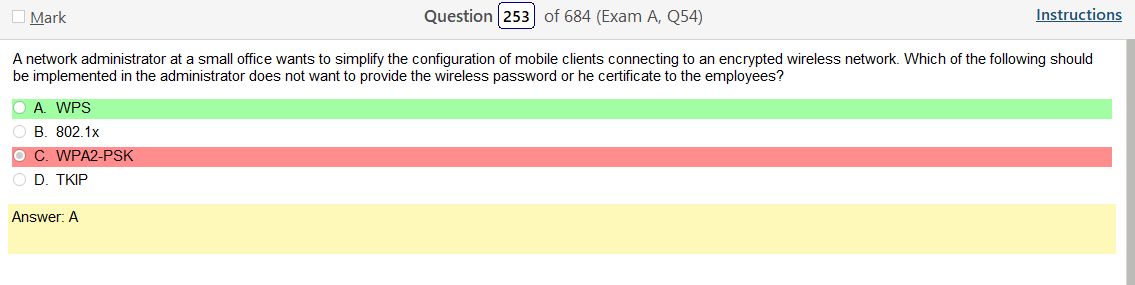
Well, for starters, anything is better than WEP. Im not really seeing any legacy choices right away but I did pick WPA2 Enterprise. However, I still want to go over this stuff.
- WEP – a security algorithm for IEEE 802.11 wireless networks. Introduced as part of the original 802.11 standard ratified in 1997, its intention was to provide data confidentiality comparable to that of a traditional wired network.[1] WEP, recognizable by its key of 10 or 26 hexadecimal digits (40 or 104 bits), was at one time widely in use and was often the first security choice presented to users by router configuration tools.[2][3] In 2003 the Wi-Fi Alliance announced that WEP had been superseded by Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). In 2004, with the ratification of the full 802.11i standard (i.e. WPA2), the IEEE declared that both WEP-40 and WEP-104 have been deprecated.[4] WEP was the only encryption protocol available to 802.11a and 802.11b devices built before the WPA standard, which was available for 802.11g devices. However, some 802.11b devices were later provided with firmware or software updates to enable WPA, and newer devices had it built in
- WPA and TKIP – TKIP (the basis of WPA) has reached the end of its designed lifetime, has been partially broken, and had been officially deprecated
- WPS with a pin – Created by the Wi-Fi Alliance and introduced in 2006, the goal of the protocol is to allow home users who know little of wireless security and may be intimidated by the available security options to set up Wi-Fi Protected Access, as well as making it easy to add new devices to an existing network without entering long passphrases. Prior to the standard, several competing solutions were developed by different vendors to address the same need.[1] A major security flaw was revealed in December 2011 that affects wireless routers with the WPS PIN feature, which most recent models have enabled by default. The flaw allows a remote attacker to recover the WPS PIN in a few hours with a brute-force attack and, with the WPS PIN, the network’s WPA/WPA2 pre-shared key (a.k.a. PSK).[2] Users have been urged to turn off the WPS PIN feature,[3] although this may not be possible on some router models
- WEP and RC4 – Because RC4 is a stream cipher, the same traffic key must never be used twice. The purpose of an IV, which is transmitted as plain text, is to prevent any repetition, but a 24-bit IV is not long enough to ensure this on a busy network. The way the IV was used also opened WEP to a related key attack. For a 24-bit IV, there is a 50% probability the same IV will repeat after 5,000 packets. In August 2001, Scott Fluhrer, Itsik Mantin, and Adi Shamir published a cryptanalysis of WEP[13] that exploits the way the RC4 ciphers and IV are used in WEP, resulting in a passive attack that can recover the RC4 key after eavesdropping on the network. Depending on the amount of network traffic, and thus the number of packets available for inspection, a successful key recovery could take as little as one minute
- WPA2 Enterprise – IEEE 802.11i-2004, or 802.11i for short, is an amendment to the original IEEE 802.11, implemented as Wi-Fi Protected Access II (WPA2). The draft standard was ratified on 24 June 2004. This standard specifies security mechanisms for wireless networks, replacing the short Authentication and privacy clause of the original standard with a detailed Security clause. In the process, the amendment deprecated broken Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), while it was later incorporated into the published IEEE 802.11-2007 standard. 802.11i supersedes the previous security specification, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), which was shown to have security vulnerabilities. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) had previously been introduced by the Wi-Fi Alliance as an intermediate solution to WEP insecurities. WPA implemented a subset of a draft of 802.11i. The Wi-Fi Alliance refers to their approved, interoperable implementation of the full 802.11i as WPA2, also called RSN (Robust Security). 802.11i makes use of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) block cipher, whereas WEP and WPA use the RC4 stream cipher.[1]
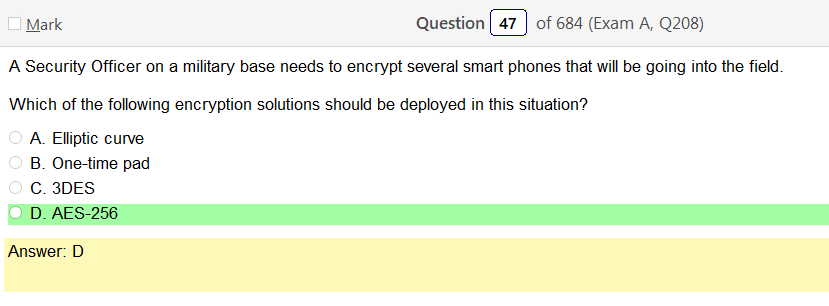
Yeah, once your figure this one out WPS2 Enterprise, which uses AES is clearly the way to go. I guess it is good to learn about legacy stuff but its so much info!!!
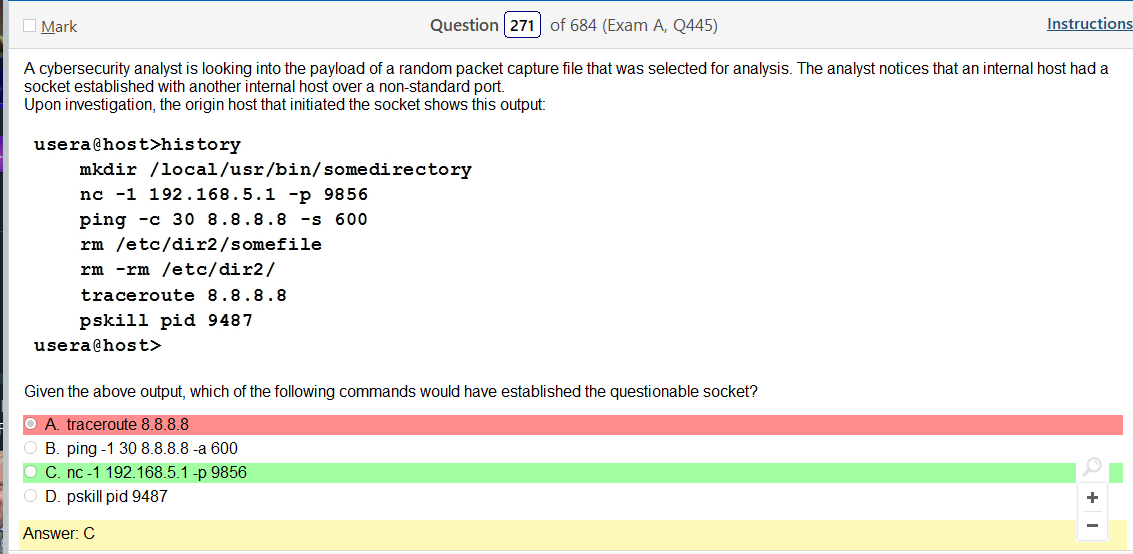
I really don’t understand what file system or operating system uses this stuff and that would be super helpful information. Like, rather than learning random shit what if it was like so your using Solarus as a file share you need to connect over a network via ssh how do you set up the share and permissions. Just a thought. Anyway, lets take a look at this one.
- SELinux mode set to enforcing- SELINUX: Set enforcing and permissive modes for SELinux
- SELinux mode set to permissive – see previous link
- FACL added –
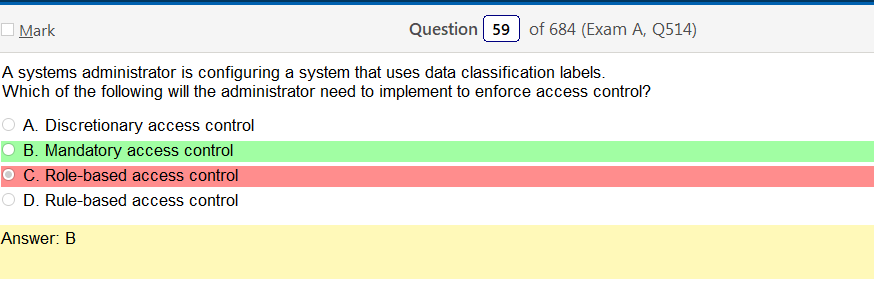
Ok, so the answer does say Linux in it but there are so many flavors! To be honest it does look like something you would find in Linux but its not like a line of code. This is also kind of A cop out because that also would probably vary by flavor. Lots of variables here but it would be more helpful than running into work and describing some sort of completely useless theory of types of permissions.
Oh man, after looking at that last one they are selling me on a Linux+ because that is fun and relevant! Ok, so I was sort of wrong and that the answer is there if you know what your looking at and if you google stuff, there are answers! It’s amazing that research exists.
- non-persistent configuration – Understanding nonpersistent vs. persistent VDI
- continuous monitoring – see above
- Firmware updates – im not defining this
- Fault tolerance – meaning that you have a fail over cluster
This question doesn’t make any sense. It says nothing about VDIs but that’s what the answer loops back to. Is a VDI a ‘critical system’ not likely.
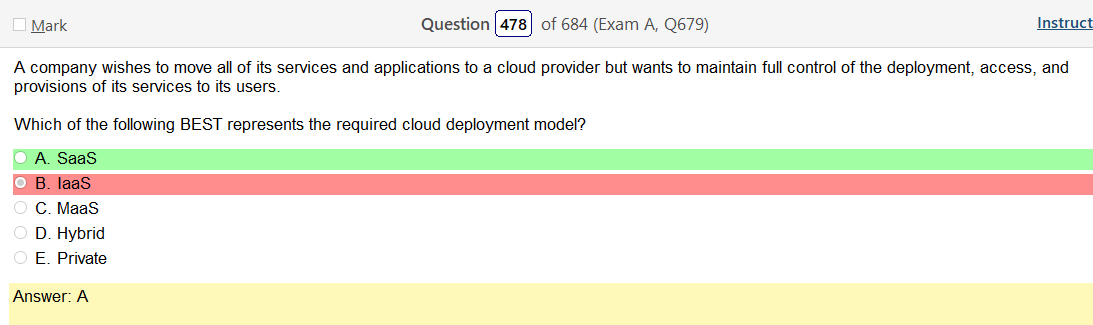
Thats just using infrastructure. Software as a service implies that your using like some application, like Salesforce. Software as a service is a software licensing and delivery model in which software is licensed on a subscription basis and is centrally hosted. This answer is straight out wrong haha
Anyway, that’s all for today. Guess I should get some sleep.